
Primary markets are where issuers sell securities to investors for the first time. Although not widely accessible, they impact the price of stocks and bonds, so it’s important to understand how they work. Read on to find out more.
What is the primary market for stocks?
The primary market for stocks is the source of newly listed securities. It’s where companies and governments attempt to gain financing through equity and debt.
Examples of securities sold on the primary market include common and preferred stock, corporate bonds and government bonds.
The sale occurs between an investor and the issuer, usually with an investment bank working as an intermediary – known as an underwriter. The issues are highly regulated by bodies such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the US.
In theory, primary markets are the first opportunity the public has to buy an asset – but for the most part, the sales are only available to institutional investors. Once the initial sale is complete, investors can sell the asset on the secondary market to retail clients.
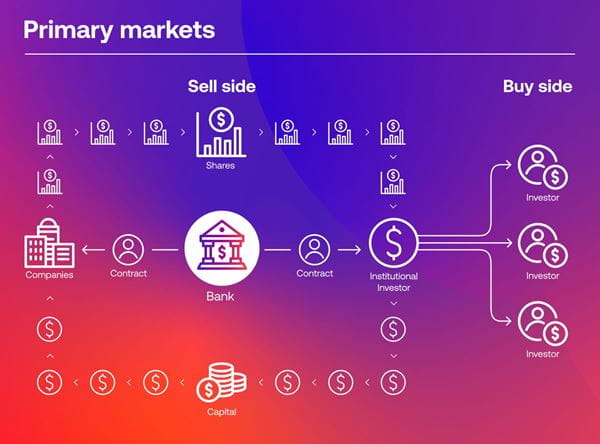
Types of primary market issues
There are several different types of primary market equity issues, including:
- Initial public offering (IPO) – this is when a company sells shares of its stock for the first time. It’s also known as ‘going public’ as the process turns a private company into a publicly traded one. Its shares will then start trading on whichever stock exchange it chooses to list on
- Rights issue – this action permits companies to raise further equity on the primary market, even if its shares are already trading on the secondary market. Existing investors will get offered a special price in proportion to their current shareholding
- Private placement – which allows companies to sell shares to its larger investors, such as hedge funds and banks, without offering the issue to the public
- Preferential allotment – gives companies the chance to offer shares to certain investors at a discounted price
Governments and companies can also issue debt on the primary market in the form of bonds.
New bonds are issued with interest (coupon) rates at the going base rate of a country. Bond issuances can significantly impact the price of older bonds, as their price can deteriorate if the newer bonds come with a higher interest rate.
Discover what interest rate risk is
Difference between primary and secondary market
The main difference between a primary and secondary market is who is offering the assets for sale. In the primary market, transactions occur between an issuer and an investor, but in the secondary market, transactions take place between two investors.
When discussing financial markets, it’s largely this segment, in which assets trade openly. It’s made up of stock exchanges, commodity exchanges and so on.




