Trading with City Index
Guide to orders
What is an order?
An order is an instruction to execute a trade when the price of a market reaches a trigger value set by you. Orders can help you to be flexible with your trading decisions and support a range of different trading strategies. They should be a key part of your risk management strategy.
City Index offers a range of different types or orders which can:
- Close existing positions
- Open new positions
In this chapter, we look at using orders as risk management tools to close active trades. These include:
- Stop losses
- Limit orders
- Trailing stops
- Guaranteed stops
- OCOs
- If-dones
Stop loss order
A stop loss order can be used to automatically close a trade at a worse price than the currently available price of a market, normally for a loss. Stop loss orders are a key tool in helping you minimise your losses if a price moves against you.
| Scenario | Long example | Short example |
|---|---|---|
| You open a position on ABC index | Go long 10 CFDs at 4250 | Go short 10 CFDs at 4000 |
| You want to place a stop loss to close out your position with a loss of 50 points | Place a stop loss at 4200 | Place a stop loss at 4050 |
| The market moves 100 points in the next 3 days | Your stop loss is triggered at 4200 | Your stop loss is triggered at 4050 |
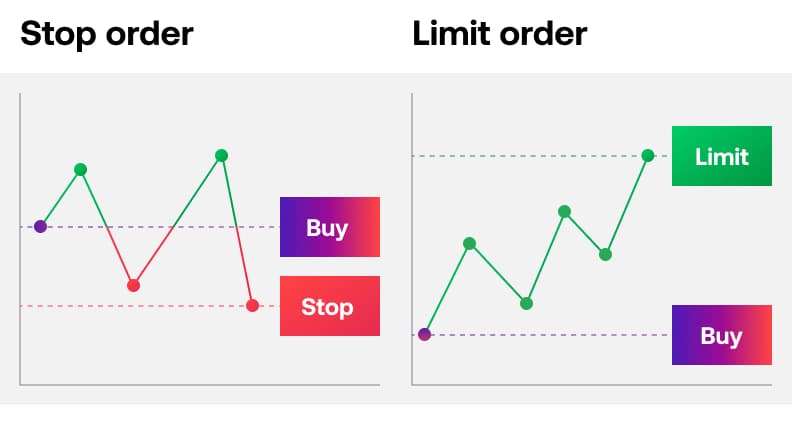
Limit order
Limit closing orders are set to automatically close a trade at a better price than the current available price of a market, locking in any profit. This helps you to be disciplined with your trading strategy and not chase profits unnecessarily.
| Scenario | Long example | Short example |
|---|---|---|
| You open a position on ABC index | Go long 10 CFDs at 4250 | Go short 10 CFDs at 4000 |
| You want to place a limit order to close out your position with a profit of 50 points | Place a limit order at 4300 | Place a limit order at 3950 |
| The market moves 100 points in the next 3 days | Your stop loss is triggered at 4300 | Your stop loss is triggered at 3950 |
| Your profit/loss | £500 profit | £500 profit |
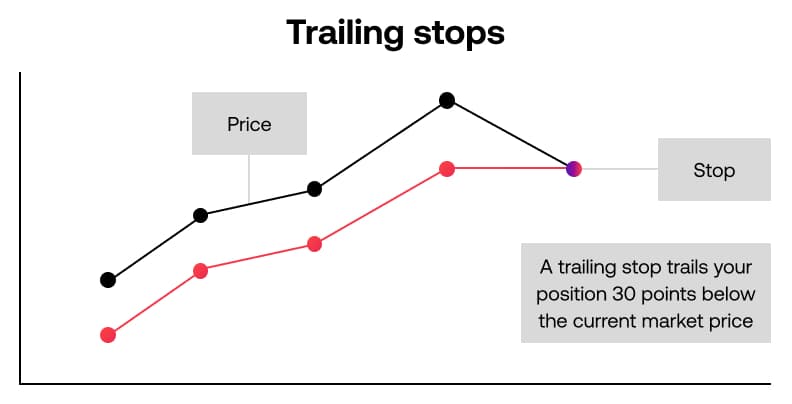
Trailing stop
Like a regular stop loss order, a trailing stop is set a specific number of points away from the current market price. When the market moves with your position, the stop setting automatically changes so that it trails the current price by the number of points you set. When the market moves against your position, the stop remains set at the last trailing price reached when the market was moving your way. You can use this to protect profits without limiting potential gains.
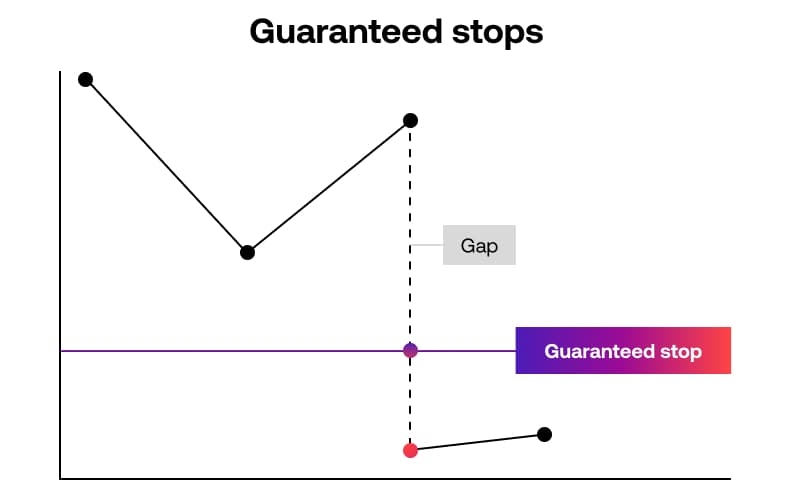
Guaranteed stop order (GSO)
Guaranteed Stop Loss Orders (GSLOs) ensure that the level at which an order will be executed is the exact level that you’ve specified, regardless of any gapping in the market.
Key features of our Guaranteed Stop Loss Orders:
- We only charge a premium for Guaranteed Stop Loss Orders if the stop is triggered
- You can amend a Guaranteed Stop Loss Order during market trading hours for no extra charge
- There is a minimum distance for orders to be placed above and below the quoted price
Guaranteed Stop Loss Orders are useful if you are trading in volatile markets or if you want to protect your initial deposit. They are not available on all City Index markets.
One cancels other (OCO)
An OCO allows you to set both a stop and a limit order at the same time. When market movements cause either order to be filled, the unfilled order is automatically cancelled. Traders often use this to protect a market order.
If you do not place an OCO, and set stops and limits independently of each other, the other order will not be cancelled if one is triggered.
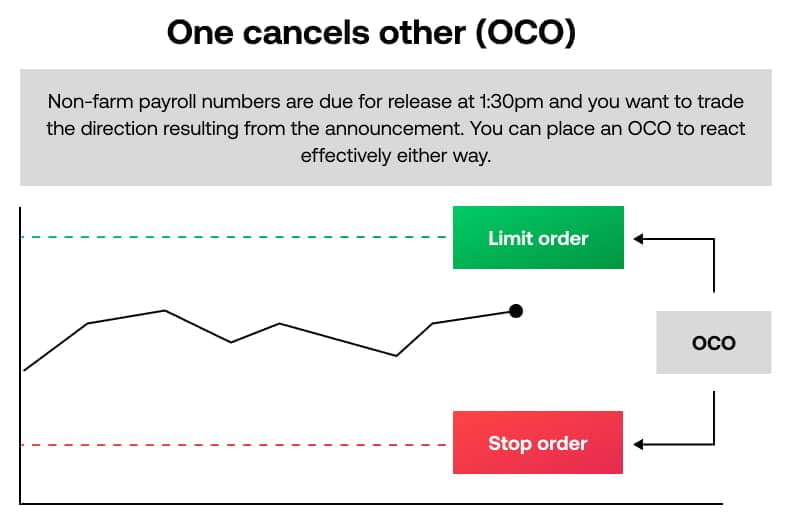
Imagine non-farm payroll numbers are due for release at 1:30pm. You think the numbers will be positive and have a long a position. You want to protect your long position, should the market not move in your favour, but also place a limit order to close your position out at a profit, should the market move in your favour.
The market is currently at 5,500, so you place an OCO: A stop to sell at 5,450 and a limit to sell at 5,550. This way, whichever order is hit first will execute and the other order will be cancelled.
'If-done' orders
Also known as contingent orders, these are closing orders attached to opening orders that are activated once the opening order has been executed.